TQM and Business ethics

TQM and business ethics have been discussed in different studies, (Svensson & Wood (2005), Wicks (2001), Jones E (2014)). In fact, Jones E. (2014) studied the relationship between TQM, ethics, and corporate social responsibility. Ethics is acting correctly with respect to a moral framework. Ethical conduct is always faced by human personal interests, where human personal interests prevail over ethical behavior. Total quality management relies on ethical conduct like building trust, communication, interpersonal relations, conflict management, problem-solving, teamwork, employee involvement and empowerment, and customer focus. This makes ethics important for a Total quality management program.
Building Trust with customers and also employees is important for successful TQM implementation. In order to achieve this, you need to be loyal, fulfill your commitments toward clients, and apologize when needed. A company should set its core values and stick to them. These values guide the company and employees to meet total quality management program goals. Individuals and organizations act according to values they believe in. Management has the responsibility to provide an environment with values that help achieve desired performance while conducting ethical behavior. Integrity includes honesty, dependability. Employees with this quality can be reliable, do the right things on time and correctly. Accepting responsibility is part of ethical behavior. People who pass blame are not behaving ethically. In a total quality management methodology, people are responsible for their performance. Values are beliefs that guide our actions. Individuals and organizations devote their efforts and energy in things they believe in. Managers are protectors of ethics in a company. They give the example of ethical behaviour, helping employees behave ethically, and take ethical decisions.
The firm’s role consists of establishing an ethical environment and providing an ethical example. To achieve this, it has to set a comprehensive ethics policy. The firm should give an example by setting the policy, expecting all employees to follow the policy, and rewarding those who do. Management set in the company qualities like trust, integrity, and a sense of responsibility in the company. People sometimes make unethical decisions because of self-interest, self-protection, conflicting values, or because they see the benefits as being intangible or deferred while they believe in ethical values set by the company.
Total quality management and total quality environmental management
There is a strong relationship between TQM and the environment, Borri and Boccaletti (1995). In a company where TQM is implemented everybody already adheres to a sustainable business, where all employees work together to reduce the company’s impact on the environment. The relationship between TQM and environment has been discussed in different studies, (Abbas J. (2020), Chen et al. (2020), Isaksson R. (2006), Reed et al. (2000), Lagrosen S. (2007), Borri and boccaletti (1995)). Today companies are forced to use innovative tools and ideas in order to answer market needs and to face rapid technology change. TQM is used to manage systems and processes and it is now extended to manage environmental processes. This is important for the business and the world. Companies have to integrate environmental challenges in their strategy to be more innovative. When a company decides to undertake a total quality management environmental program, it should have the necessary tools to tackle different environmental challenges. In a similar process other components are added to the outputs, which is the amount of emissions and waste. In a similar approach, this component has been added. Companies have to balance between efficiency, economy and quality of products while taking care of the environment. Now, many companies integrate the respect of the environment in their process. Borri and Boccaletti (1995) in their work explained how to integrate the environment component in a total quality management program.
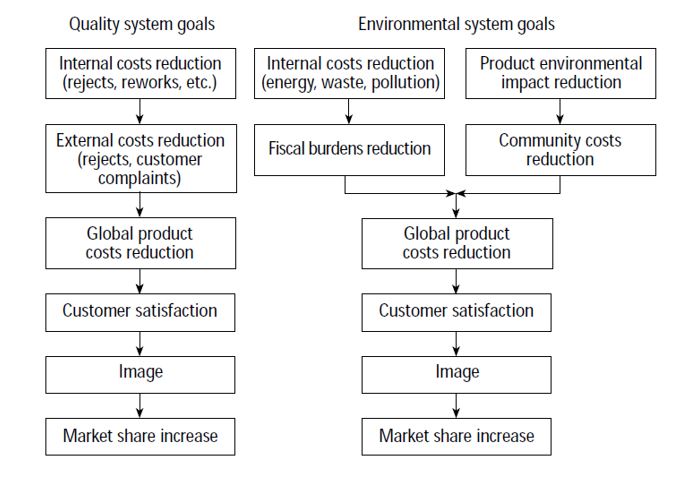
Correlation between quality and environmental management system. Source: Borri and Boccaletti (1995).
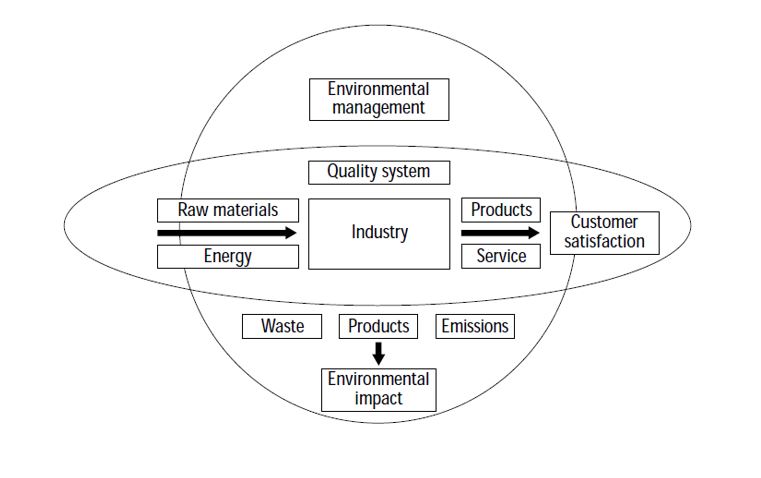
Quality and environmental parallelism. Source: Borri and Boccaletti (1995).
Quality management systems aim to meet customers’ needs; however, environmental management systems focus not only on customers’ needs but also on different stakeholders (regulators, government, communities, investors), (Tari and Molina-Azorin (2010), Klefsjö et al. (2008)). In environmental system, the company considers the direct and indirect impact on the surroundings and users during the entire product life-cycle, (Borri and Boccaletti (1995), Klassen and McLaughlin (1993)).
Borri and Boccaletti (1995) established a comparison between TQM and TQEM and presented a list of analogies (employee education, management commitment, continuous improvement and customer focus):
- In term of employee education, TQEM focus on environmental seminars, environmental suggestion program.
- In a TQEM program, CEO elaborates an environmental strategy that reflects management commitment.
- Continuous improvements in a TQEM program consist on adopting ecological standards and also on being proactive and cooperate with local authorities.
- In a TQEM, customer focus consists on controlling customer perception of the company, monitoring end of life products disposal.
The integration of the environment element in a quality management program has proved its benefit. It improves efficiency and productivity, eliminates unproductive waste entering the environment, reduces potential barriers to entry (certifications), and prevents potential environmental incidents and future liabilities. Moreover, TQEM (total quality environmental management) supports partnership with customers, suppliers to answer environmental needs, (Borri and Boccaletti (1995), Klassen and McLaughlin (1993), Tari and Molina-Azorin (2010)).
The way to deal with different environmental challenges differs according to the management approach. It could be a passive, active or proactive approach (Borri and Boccaletti 1995). In a passive approach, engineers are responsible for reducing emissions and waste. The reason is to reduce costs of these activities. In an active approach, middle management is responsible to comply with environmental regulation. The management aims to improve the process in order to reduce the impact on the environment. Finally, the proactive approach where a total quality management approach is adopted and everybody contributes to reduce the impact of the company on the environment.


